Early detection saves lives!
With your breast scan, you will receive 5 images. Thermography’s role is to provide early detection of breast cancer, and other breast diseases, by monitoring abnormal physiology and establishment of risk factors for the development or existence of cancer. Thermography offers the opportunity of earlier detection of breast disease than has been possible through breast self examination, doctor examination or mammography alone. Early detection of breast cancer leads to increased survival rates!
How does thermography detect breast cancer?
A thermography scan detects subtle physiological changes that accompany breast pathology, whether it is cancer, fibrocystic disease, an infection or vascular disease. Your doctor can then plan accordingly, and lay out a careful program to further diagnose and/ or MONITOR you during and after treatment.
Thermography and dense breast tissue
All women can benefit from thermography. However, it is especially appropriate for younger women (ages 30-50) whose denser breast tissue makes it more difficult for mammography to be effective. It is also appropriate for women of all ages who, for many reasons, are unable to undergo routine mammography. This test can provide a “clinical marker” to the doctor or mammographer that a specific area of the breast needs particularly close attention.
Your first breast screening session helps provide a baseline of your “thermal signature”. A subsequent session 3 months later assures that the patterns remain unchanged and finishes your baseline. Annual visits are recommended after the baseline is established.
Is thermography accurate?
Yes! You do need to have a stable thermal pattern established though. All of your breast thermograms are kept on record, and once your stable thermal pattern has been established any changes can be detected during your routine annual studies. This is how thermography detects breast cancer and other breast diseases, and is also why thermography is phenomenal as an early breast cancer detection method.
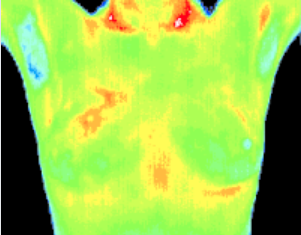
Baseline
Baseline thermogram showed a slight hyperthermic asymmetry in the upper right breast.
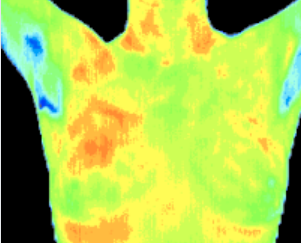
3 Months
The follow up study at 3 months showed the pattern had become more well defined. Mammography was inconclusive.
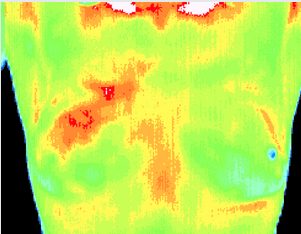
12 Months
Significantly increased vascular changes. Repeat mammography showed a small calcification (1 mm) at 1 o'clock. A lumpectomy was performed confirming a malignant carcinoma (DCIS).
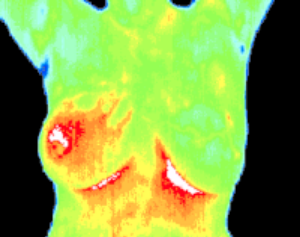
Inflammatory Cancer
There were no visible signs of abnormality. Referral to a breast specialist and a subsequent biopsy diagnosed inflammatory breast cancer at a very early stage.
Fibrocystic
Significant vascular activity in the left breast which was clinically correlated with fibrocystic changes.
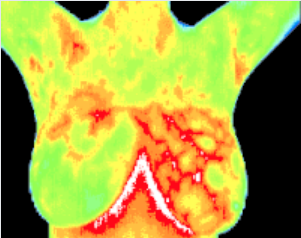
Ductal Carcinoma
The vascular asymmetry in the upper left breast was particularly suspicious and clinical investigation indicated a palpable mass. A biopsy was performed and a DCIS os 2 CM was diagnosed.
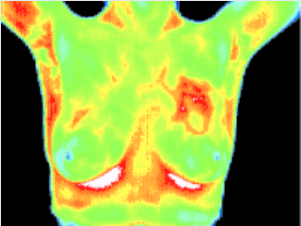
Active cancer cells double in number every 90 days.
90 Days
1 Year
2 Years
3 Years
4 Years
5 Years
6 Years
7 Years
8 Years
4 doublings (approximately 10 years) is considered lethal.
It takes years for a tumor to grow. The earliest possible indication of abnormality is needed to allow for the earliest possible treatment and prevention. With breast cancer, early detection can mean treatment for stage 1 breast cancer opposed to more progressed breast cancer stages.
Breast cancers seem to grow significantly faster in women under 50; causing breast cancer stages to progress more rapidly.
| Age | Average tumor doubling time |
|---|---|
| Under 50 | 80 Days |
| 50-70 | 157 Days |
| Over 70 | 188 Days |
